Cancer chemotherapy may be associated with a high incidence of nausea and vomiting, particularly when highly emetogenic antineoplastic drugs are used. Uncontrolled emesis can profoundly impact on the patient's quality of life and ability to survive, by causing dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, malnutrition and treatment discontinuation.
The ABVD regimen (Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine and Dacarbazine) is considered the standard of care for first-line treatment of Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Among these drugs, dacarbazine and adriamycin are the most emetogenic, being classified as highly and moderately emetogenic chemotherapy, respectively.
NEPA is the first fixed antiemetic combination composed by the pharmacologically and clinically distinct 5HT3 receptor antagonist (5HT3-RA) palonosetron and the highly selective Neurokinin1/Substance P receptor antagonist (NK1-RA). A single dose of NEPA per chemotherapy cycle acts on the principal pathways involved in the mechanisms controlling nausea and vomiting in a synergistic way with an appropriate half-life to cover both the acute (0-24 hours from chemotherapy) and delayed (25-120 hours) phase.
In this open label multicenter study, chemo-naïve Hodgkin's Lymphoma patients who were addressed to receive their first cycle of ABVD regimen (2 doses in 28 days, on days 1 and 15) were given a single administration of NEPA plus 4 mg dexamethasone. The primary endpoint was complete response (CR), defined as no emesis and no rescue medication during the overall phase (0-120 hours) on the first dose of the first ABVD cycle.
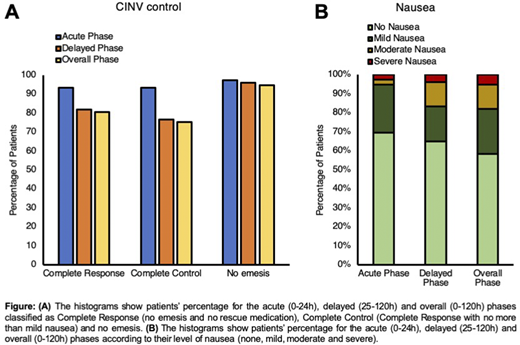
A total of 77 patients were evaluated. According to the adopted Fleming one-stage design, the primary endpoint of this study was achieved. Indeed, the number of the complete responders for the overall phase among the first 70 consecutive patients was 66, which is greater than the pre-determined cut-off of 46, representing the minimum frequency of responders for which the treatment is considered effective. In addition to the primary efficacy endpoint, several additional endpoints were evaluated. The CR values were 93.5% for the acute phase, 81.8% for the delayed phase and 80.5% for the overall phase, while Complete Control (CR with no more than mild nausea) were achieved in the 93.5%of patients in the acute phase, 76.6% in the delayed phase and 75.3% in the overall phase (Figure 1A). Also, levels of no significant nausea (no more than mild nausea) were 94.6% for the acute phase, 83.1% for the delayed phase and 81.8% for the overall phase (Figure 1B).
This study demonstrated the efficacy of NEPA plus dexamethasone in preventing the nausea and vomiting induced by the highly emetogenic ABVD regimen.
Abruzzese:Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bms: Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Di Renzo:BerGenBio ASA: Research Funding. Flenghi:takeda: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; janssen-cilag: Consultancy; teva: Consultancy; Servier Italia: Consultancy. Cantonetti:Vifor: Consultancy; Mundipharma: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal